The electric vehicle trend in Indonesia is an inevitability. This means that sooner or later, the existence of environmentally friendly four-wheeled and two-wheeled vehicles will grow rapidly in Indonesia. In fact, many automotive manufacturers have started marketing or developing electric cars or motorcycles for the national market.
Broadly speaking, electric vehicles circulating in Indonesia are divided into three types: hybrid, plug-in hybrid (PHEV), and pure electric or battery.
All of these types of electrification technology offer different efficiencies, performance, and carbon emission reductions. So, to find out the differences between these three environmentally friendly technologies, let's discuss them one by one, as reported from various sources.
Hybrid Car


The first technology discussed is hybrid cars. This type of vehicle is still the most widely circulated in Indonesia. Various manufacturers have hybrid line-ups for the Indonesian market. Just mention Toyota, which has the Innova Zenix hybrid, Corolla Cross hybrid, Camry hybrid, and Yaris Cross.
Meanwhile, Suzuki has the Ertiga hybrid, the XL7 hybrid, and the Grand Vitara hybrid. Then, there is the Wuling Almaz RS hybrid. Apart from that, luxury brands such as Lexus also do not escape competition from the hybrid segment by offering the ES 300h.
If we talk about hybrid technology, it is a combination of power sources originating from a conventional engine (gasoline or diesel) combined with an electric motor.
Hybrid cars can be driven using just an electric motor, a conventional engine, or a combination of both.
How it works is that electric motors and conventional engines can be used alternately or simultaneously to move the vehicle's wheels.
Meanwhile, the batteries in hybrid cars usually have a small capacity, and can be recharged when the driver is braking. This is different from plug-in hybrid or PHEV) and electric cars, which require separate power or charging the battery using a special tool, either at home or at a public electric vehicle charging station(SPKLU).
PHEV
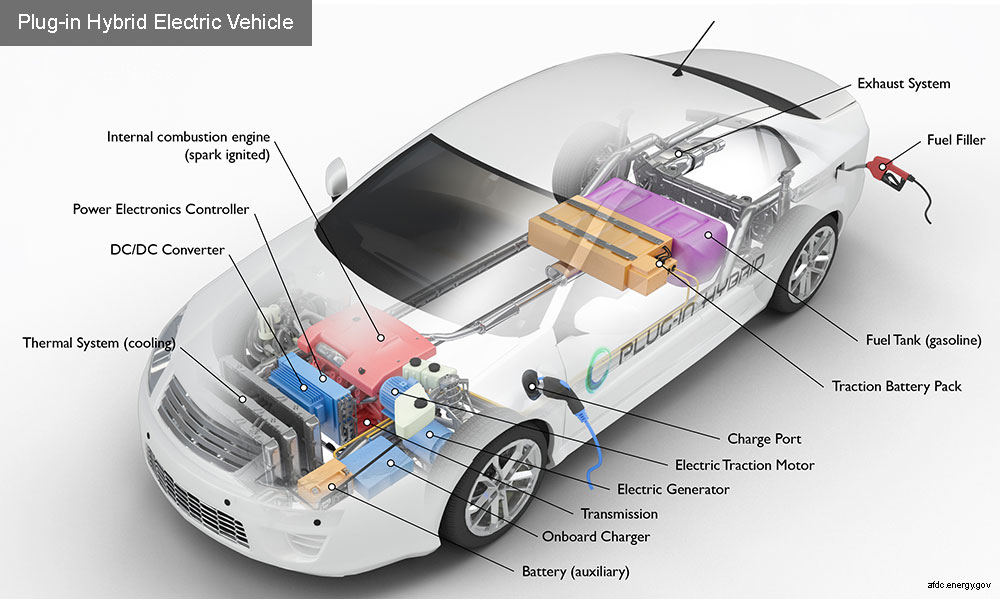

In short, hybrid cars and PHEVs do not make much difference. This technology still relies on conventional engines and electric motors, with the help of batteries.
The difference is the larger battery capacity for PHEV-type cars. With a larger battery capacity, it allows the engine to work more efficiently and can use one of the drives if a problem occurs with the other drive
Apart from that, the next fundamental difference is the way the battery is charged in a PHEV car. For hybrid cars, you can charge the battery by braking, but for PHEVs, it must be done manually or plug-in from an electricity source, either from a wall charger installed at home or in the office, and you can also use public electric vehicle charging stations. (SPKLU).
Like a hybrid car, because it still has a conventional engine, the PHEV's four wheels must also be filled with fuel to move the conventional engine while driving.
Electric Cars

Lastly, there are pure electric cars, aka batteries, which have the most significant difference compared to the two technologies discussed previously. As the name suggests, a pure electric car only relies on an electric motor to move the wheels and a battery as a power source.
This type of car, of course, no longer needs fuel because, to charge it, you have to charge electricity via a wall charger installed at home or use an existing SPKLU. Apart from that, in terms of driving capacity, pure electric or battery cars can travel between 200 and 500 km.
But, keep in mind once again, this mileage of course varies from one brand to another, as do the models launched by each manufacturer.
So, the three types of electrified vehicles, whether hybrid, PHEV, or pure electric, have different ways of working. Likewise with efficiency, performance, distance traveled, and the charging method between one type of vehicle and another.
Sources : Insideevs, Autoblog, and Auto2000
Foto via Insideevs
